区块链技能英文,Introduction to Blockchain Technology
Introduction to Blockchain Technology

Blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary force in the digital world, disrupting traditional industries and reshaping the way we perceive data security and transaction processing. This article aims to provide an overview of blockchain technology, its working principles, and its potential applications across various sectors.
What is Blockchain?
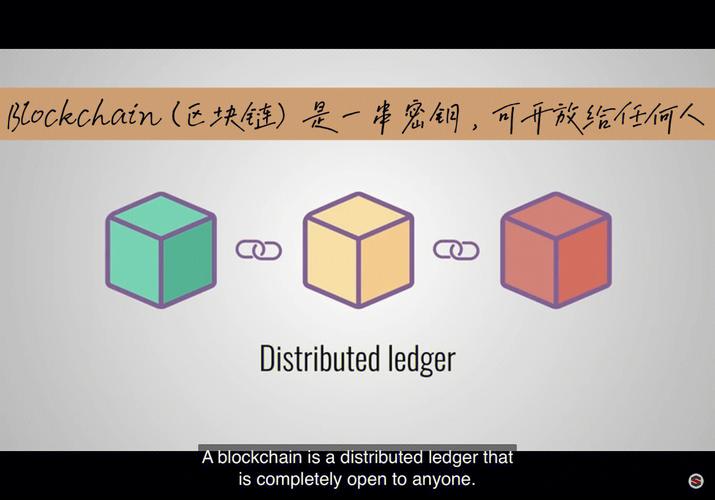
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers so that the record cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all subsequent blocks and the consensus of the network. It is essentially a chain of blocks, where each block contains a list of transactions.
Key Features of Blockchain

There are several key features that make blockchain technology unique and secure:
Decentralization: Unlike traditional centralized systems, blockchain operates on a decentralized network, ensuring that no single entity has control over the entire system.
Immutability: Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, providing a high level of security and trust.
Transparency: All transactions are visible to all participants in the network, fostering a transparent and accountable system.
Consensus Mechanism: Blockchain relies on a consensus mechanism to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain, ensuring that all participants agree on the validity of the transactions.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchain operates through a series of steps:
Transaction Creation: A transaction is created and broadcasted to the network.
Transaction Verification: Nodes in the network validate the transaction, ensuring that it meets the necessary criteria (e.g., sufficient funds, valid digital signature, etc.).
Block Creation: Once the transaction is verified, it is added to a new block along with other transactions.
Block Hashing: Each block contains a unique hash value that is generated using cryptographic algorithms. This hash value is used to link the block to the previous block in the chain.
Consensus and Block Addition: The network reaches a consensus on the validity of the block, and once agreed upon, the block is added to the blockchain.
Applications of Blockchain
Blockchain technology has the potential to transform various industries, including:
Finance: Blockchain can streamline cross-border payments, reduce transaction costs, and enhance security in financial transactions.
Supply Chain: Blockchain can provide end-to-end transparency in supply chain management, ensuring the authenticity and traceability of products.
Healthcare: Blockchain can securely store and share patient records, improving data integrity and privacy.
Real Estate: Blockchain can simplify property transactions, reduce fraud, and provide a transparent record of ownership.
Government: Blockchain can enhance the efficiency and transparency of government services, such as voting and land registration.
Challenges and Future Outlook

While blockchain technology offers numerous benefits, it also faces several challenges:
Scalability: Blockchain networks can struggle to handle a large number of transactions simultaneously, leading to slower processing times and higher costs.
Energy Consumption: The consensus mechanisms used by some blockchain networks, such as Proof of Work (PoW), consume a significant amount of energy.
Regulatory Hurdles: The evolving nature of blockchain technology makes it challenging for governments and regulatory bodies to keep up with the pace of innovation.
Despite these challenges, the future of blockchain technology looks promising. As the technology continues to evolve and overcome these obstacles, it is expected to play a crucial role in shaping the future of various industries.
Conclusion

Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with data and conduct transactions. By offering a decentralized, secure, and transparent system, blockchain can bring numerous benefits to various industries. As the technology continues to
猜你喜欢
 其他
其他
开源库房办理体系,开源库房办理体系的兴起与价值
1.GreaterWMS特色:彻底开源,遵从ApacheLicense2.0协议,前后端别离,支撑多仓、波次发货、兼并拣货等事务模型。2.InvenTree特色:高度通用且可定制开发,支撑多库房、多货位、多批次办理,...
2024-12-25 1 其他
其他
深圳区块链开发公司,引领数字经济新时代
以下是几家坐落深圳的区块链开发公司及其基本信息:1.区块链科技(深圳)有限公司建立日期:2013年10月17日地址:深圳市南山区粤海大街科技园大厦899A经营范围:云核算、人工智能、区块链技能开发、大数据及智能投顾...
2024-12-25 1 其他
其他
安卓开源是什么意思,安卓开源是什么意思?揭秘开源背面的故事
安卓开源指的是安卓操作体系(Android)的源代码是揭露的,任何人都可以自由地检查、修正和分发这些源代码。安卓是由谷歌主导开发的开源移动操作体系,它依据Linux内核,采用了Apache答应证。这意味着,开发者可以在恪守答应协议的前提下,...
2024-12-24 3 其他
其他
区块链发票查验,安全、高效、快捷的电子发票真伪辨认办法
1.国家税务总局全国增值税发票查验渠道:拜访https://invveri.chinatax.gov.cn/输入需求查询的增值税电子普通发票的相关信息,承认输入的信息无误后,点击“查验”按钮即可得到真伪成果。2.当地税务...
2024-12-24 2 其他
其他
obs开源代码,架构、功用与定制开发
1.项目简介:OBSStudio是一款用于视频录制和直播的开源软件,支撑Windows、Mac和Linux等多个渠道。它支撑多种视频源和场n2.技能栈:OBSStudio的源码首要运用C编写,并选用...
2024-12-24 4 其他
其他
合肥云核算训练,敞开数字化转型的钥匙
在合肥,有多家组织供给云核算训练课程,以下是几家首要的训练组织及其课程设置:1.合肥北大青鸟校园课程内容:绵亘企业网络通信与Linux使用、大型网站架构优化与高可用、虚拟化与云渠道、云端主动化运维与DevOps、云安全等。...
2024-12-24 2 其他
其他
云核算的云,界说与概述
云核算(CloudComputing)是一种通过互联网供给核算资源(如服务器、存储、数据库、网络、软件、剖析等)的方式,用户能够按需获取这些资源而无需购买或维护相关硬件和软件。这种方式使得用户能够灵敏地扩展或减缩资源运用,并依据实践运用量...
2024-12-24 2 其他
其他
区块链抽奖,区块链技能革新抽奖职业,打造公平公平的抽奖体会
区块链抽奖是一种使用区块链技能进行抽奖活动的方法。它具有以下几个特色:1.公平性:区块链抽奖使用区块链的不行篡改性,确保抽奖进程和成果的公平性。一切参加者的抽奖号码和成果都会被记载在区块链上,无法被篡改,确保了抽奖的公平性。2.通明性:...
2024-12-24 2

